Competitive H2S–CO2 absorption in reactive aqueous methyldiethanolamine solution: Prediction with ePC-SAFT
Abstract
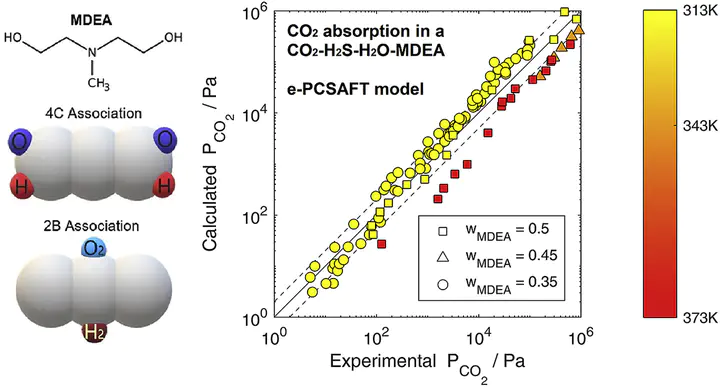
Reactive absorption of CO2 and H2S in aqueous methyldiethanolamine (MDEA) solutions is considered within the ePC-SAFT equation of state. We demonstrate that ePC-SAFT can be employed in a predictive manner without regression of additional temperature-correlated terms. Mixed system predictions are tested using a consistent set experimental data covering a wide range of temperatures (313K – 413K), partial pressures (0.001 kPa – 1000 kPa), and MDEA mass fractions (5 wt.% – 75 wt.%). Predicted partial pressures for acid gas absorption show good agreement for low MDEA fractions (< 50 wt.%). Absorption selectivity in binary H2S + CO2 absorption is correctly predicted, with absolute average deviations of 57.18% and 79.32% for partial pressures of CO2 and H2S. We identify a significant deterioration in ePC-SAFT predictive power for the high-MDEA regime (> 50 wt.%), likely originating from underlying assumptions in the Debye-Hückel electrolyte free energy treatment and representation of ionic species.